A) It is very rapid over long distances.
B) It requires an expenditure of energy by the cell.
C) It is a passive process in which molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration.
D) It is an active process in which molecules move from a region of lower concentration to one of higher concentration.
E) It requires integral proteins in the cell membrane.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the voltage across a membrane called?
A) water potential
B) chemical gradient
C) membrane potential
D) osmotic potential
E) electrochemical gradient
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the following questions, match the labelled component of the cell membrane in the figure with its description.
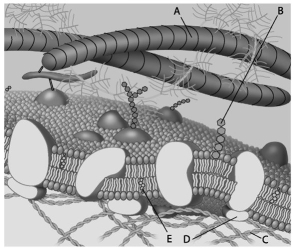 -Which component is the peripheral protein?
-Which component is the peripheral protein?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An organism with a cell wall would most likely be unable to take in materials through
A) diffusion.
B) osmosis.
C) active transport.
D) phagocytosis.
E) facilitated diffusion.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
White blood cells engulf bacteria through what process?
A) exocytosis
B) phagocytosis
C) pinocytosis
D) osmosis
E) receptor-mediated exocytosis
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following processes includes all others?
A) osmosis
B) diffusion of a solute across a membrane
C) facilitated diffusion
D) passive transport
E) transport of an ion down its electrochemical gradient
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the following questions, match the labelled component of the cell membrane in the figure with its description.
 -Which component is cholesterol?
-Which component is cholesterol?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
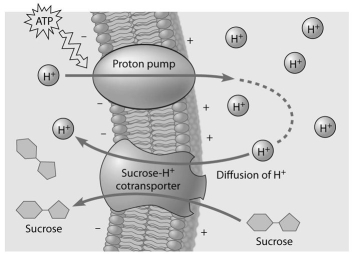 -Based on the figure above, which of these experimental treatments would increase the rate of sucrose transport into the cell?
-Based on the figure above, which of these experimental treatments would increase the rate of sucrose transport into the cell?
A) decreasing extracellular sucrose concentration
B) decreasing extracellular pH
C) decreasing cytoplasmic pH
D) adding an inhibitor that blocks the regeneration of ATP
E) adding a substance that makes the membrane more permeable to hydrogen ions
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The solutions in the arms of a U-tube are separated at the bottom of the tube by a selectively permeable membrane. The membrane is permeable to sodium chloride but not to glucose. Side A is filled with a solution of 0.4 M glucose and 0.5 M sodium chloride (NaCl) , and side B is filled with a solution containing 0.8 M glucose and 0.4 M sodium chloride. Initially, the volume in both arms is the same. Refer to the figure to answer the following questions.
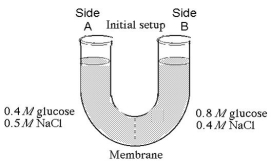 -At the beginning of the experiment,
-At the beginning of the experiment,
A) side A is hypertonic to side B.
B) side A is hypotonic to side B.
C) side A is isotonic to side B.
D) side A is hypertonic to side B with respect to glucose.
E) side A is hypotonic to side B with respect to sodium chloride.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The presence of cholesterol in the plasma membranes of some animals
A) enables the membrane to stay fluid more easily when cell temperature drops.
B) enables the animal to remove hydrogen atoms from saturated phospholipids.
C) enables the animal to add hydrogen atoms to unsaturated phospholipids.
D) makes the membrane less flexible, allowing it to sustain greater pressure from within the cell.
E) makes the animal more susceptible to circulatory disorders.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Ions diffuse across membranes through specific ion channels
A) down their chemical gradients.
B) down their concentration gradients.
C) down the electrical gradients.
D) down their electrochemical gradients.
E) down the osmotic potential gradients.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A bacterium engulfed by a white blood cell through phagocytosis will be digested by enzymes contained in
A) peroxisomes.
B) lysosomes.
C) Golgi vesicles.
D) vacuoles.
E) secretory vesicles.
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a plant cell, such as one from a peony stem, is submerged in a very hypotonic solution, what is likely to occur?
A) The cell will burst.
B) The cell membrane will lyse.
C) Plasmolysis will shrink the interior.
D) The cell will become flaccid.
E) The cell will become turgid.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The fluid mosaic model of the membrane proposes that membranes
A) are a phospholipid bilayer.
B) are a phospholipid bilayer between two layers of hydrophilic proteins.
C) are a single layer of phospholipids and proteins.
D) consist of protein molecules embedded in a fluid bilayer of phospholipids.
E) consist of a mosaic of polysaccharides and proteins.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mammalian blood contains the equivalent of 0.15 M NaCl. Seawater contains the equivalent of 0.45 M NaCl. What will happen if red blood cells are transferred to seawater?
A) Water will leave the cells, causing them to shrivel and collapse.
B) NaCl will be exported from the red blood cells by facilitated diffusion.
C) The blood cells will take up water, swell, and eventually burst.
D) NaCl will passively diffuse into the red blood cells.
E) The blood cells will expend ATP for active transport of NaCl into the cytoplasm.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The solutions in the arms of a U-tube are separated at the bottom of the tube by a selectively permeable membrane. The membrane is permeable to sodium chloride but not to glucose. Side A is filled with a solution of 0.4 M glucose and 0.5 M sodium chloride (NaCl) , and side B is filled with a solution containing 0.8 M glucose and 0.4 M sodium chloride. Initially, the volume in both arms is the same. Refer to the figure to answer the following questions.
 -If you examine side A after three days, you should find
-If you examine side A after three days, you should find
A) a decrease in the concentration of NaCl and glucose and an increase in the water level.
B) a decrease in the concentration of NaCl, an increase in water level, and no change in the concentration of glucose.
C) no net change in the system.
D) a decrease in the concentration of NaCl and a decrease in the water level.
E) no change in the concentration of NaCl and glucose and an increase in the water level.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following information to answer the questions below.
Five dialysis bags, constructed from a semipermeable membrane that is impermeable to sucrose, were filled with various concentrations of sucrose and then placed in separate beakers containing an initial concentration of 0.6 M sucrose solution. At 10-minute intervals, the bags were massed (weighed) and the percent change in mass of each bag was graphed.
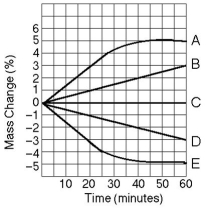 -Which line or lines in the graph represent(s) bags that contain a solution that is hypertonic at 50 minutes?
-Which line or lines in the graph represent(s) bags that contain a solution that is hypertonic at 50 minutes?
A) A and B
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) D and E
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the following questions, match the labelled component of the cell membrane in the figure with its description.
 -Initially, in terms of tonicity, the solution in side A with respect to that in side B is
-Initially, in terms of tonicity, the solution in side A with respect to that in side B is
A) hypotonic.
B) plasmolyzed.
C) isotonic.
D) saturated.
E) hypertonic.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is most likely true of a protein that cotransports glucose and sodium ions into the intestinal cells of an animal?
A) The sodium ions are moving down their electrochemical gradient while glucose is moving up.
B) Glucose entering the cell along its concentration gradient provides energy for uptake of sodium ions against the electrochemical gradient.
C) Sodium ions can move down their electrochemical gradient through the cotransporter whether or not glucose is present outside the cell.
D) The cotransporter can also transport potassium ions.
E) A substance that blocks sodium ions from binding to the cotransport protein will also block the transport of glucose.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which of the following would there be the greatest need for osmoregulation?
A) an animal connective tissue cell bathed in isotonic body fluid
B) cells of a tidepool animal such as an anemone
C) a red blood cell surrounded by plasma
D) a lymphocyte before it has been taken back into lymph fluid
E) a plant being grown hydroponically (in a watery mixture of designated nutrients)
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 78
Related Exams