A) [1] KOC(CH3) 3,[2] trans-2-butene
B) [1] KOC(CH3) 3,[2] cis-2-butene
C) [1] trans-2-butene, [2] KOC(CH3) 3
D) [1] cis-2-butene, [2] KOC(CH3) 3
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Organocuprate reagents (R2CuLi) react with several compounds. Which listed reaction isnot correct?
A) Carbon dioxide reacts with organocuprate reagents to form carboxylic acids.
B) Acid chlorides react with organocuprate reagents to form ketones.
C) Epoxides react with organocuprate reagents to form alcohols.
D) Alkyl halides react with organocuprate reagents to form coupling products containing a new carbon-carbon bond.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements isnot true about a carbene?
A) A carbene is surrounded by six electrons.
B) A carbene is sp3 hybridized.
C) A carbene contains a divalent carbon.
D) A carbene is a neutral reactive intermediate.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following isnot a step in the Suzuki reaction?
A) Transfer of the alkyl group from the organoborane to palladium
B) Reductive elimination of R-R, forming the new C-C bond
C) Oxidative addition of R-X to the palladium catalyst
D) Substitution of the R group to the palladium catalyst
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why is the Grubbs catalyst synthetically important?
A) Because it provides a synthetic pathway for ring-closing metathesis reactions
B) Because it produces only stereoselective products
C) Because it produces only stereospecific products
D) Because it only requires dilute concentrations of the reactants
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Choose the statement below that isnot true about the Suzuki reaction.
A) The Suzuki reaction forms more highly substituted alkenes.
B) The Suzuki reaction involves an oxidative addition followed by a reductive elimination.
C) The Suzuki reaction involves both an organoborane reagent and an organopalladium catalyst.
D) The product of the Suzuki reaction is completely stereospecific.
F) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Starting with chloroform, what reactions order and reagents are necessary to produce the following product? ![Starting with chloroform, what reactions order and reagents are necessary to produce the following product? A) [1] trans-2-butene, [2] KOC(CH<sub>3</sub>) <sub>3</sub> B) [1] KOC(CH<sub>3</sub>) <sub>3</sub>,[2] cis-2-butene C) [1] cis-2-butene, [2] KOC(CH<sub>3</sub>) <sub>3</sub> D) [1] KOC(CH<sub>3</sub>) <sub>3</sub>,[2] trans-2-butene](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBMG1035/11ee4665_5cf7_d12d_862d_f7912ac62226_TBMG1035_00.jpg)
A) [1] trans-2-butene, [2] KOC(CH3) 3
B) [1] KOC(CH3) 3,[2] cis-2-butene
C) [1] cis-2-butene, [2] KOC(CH3) 3
D) [1] KOC(CH3) 3,[2] trans-2-butene
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following descriptions doesnot apply to methylene?
A) Methylene is a radical intermediate.
B) The formula of methylene is :CH2.
C) Methylene is a neutral, reactive intermediate.
D) Methylene is sp2 hybridized.
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the major product of the following reaction? 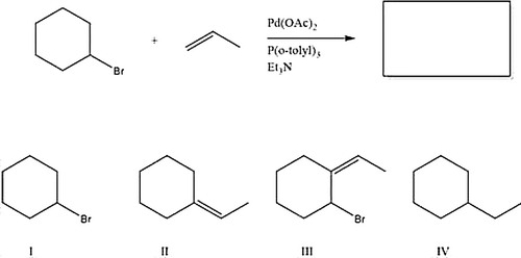
A) III
B) I
C) IV
D) II
F) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the appropriate sequence of reagents that will produce the target molecule shown below from ethylbenzene? 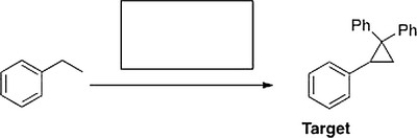
A) (1) H2SO4(aq.) , D ; (2) MCPBA; (3) CHBr3, KO(CH3) 3 ; (4) CH2=CPh2
B) (1) HBr, H2O2; (2) KOC(CH3) 3 ; (3) MCPBA; (4) CH2=CPh2
C) (1) Br2, FeBr3 ; (2) MCPBA; (3) CHBr3, KO(CH3) 3 ; (4) Ph2COCl
D) (1) NBS, hn ; (2) KOC(CH3) 3 ; (3) CHBr3, KO(CH3) 3 ; (4) a. LiCuPh2, b. H2O
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement below best explains what is meant by the statement, "An organocuprate reaction with a vinyl halide is stereospecific"?
A) The reaction of a vinyl halide with the R2CuLi reagent will only yield thecis product.
B) The reaction of a specific stereoisomer with the R2CuLi reagent will yield that particular stereoisomer as the product.
C) The reaction of a vinyl halide with the R2CuLi reagent will only yield one enantiomer product-eitherR orS configuration.
D) The reaction of a vinyl halide with the R2CuLi reagent will only yield thetrans product.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As shown below, when cis-2-butene reacts with dichlorocarbene, only the cis-1,1-dichloro-2,3-dimethylcyclopropane is formed. What can we conclude about the nature of the reaction mechanism? 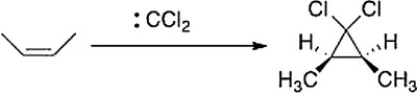
A) The mechanism is an SN1 mechanism.
B) The mechanism proceeds through a radical intermediate.
C) The mechanism is a concerted.
D) The mechanism is an E2 mechanism.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Many of the reactions studied in this chapter are stereospecific. Why are stereospecific reactions important?
A) All of the choices are true.
B) Often stereoisomers of a particular compound will have very different biological effects on an organism. Only one isomer is biologically helpful, and the other may be harmful.
C) When a reaction produces a mixture of enantiomers, it is often very difficult to separate them. A mixture of products is often not useful.
D) Often only one stereoisomer is biologically active, and coupling reactions are often used for the production of biological materials.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 13 of 13
Related Exams