A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A protein that spans the phospholipid bilayer one or more times is
A) a transmembrane protein.
B) an integral protein.
C) a peripheral protein.
D) an integrin.
E) a glycoprotein.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The solutions in the two arms of this U-tube are separated by a membrane that is permeable to water and glucose but not to sucrose. Side A is half-filled with a solution of 2 M sucrose and 1 M glucose. Side B is half-filled with 1 M sucrose and 2 M glucose. Initially, the liquid levels on both sides are equal.
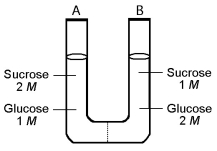 -After the system reaches equilibrium, what changes are observed?
-After the system reaches equilibrium, what changes are observed?
A) The molarity of sucrose and glucose are equal on both sides.
B) The molarity of glucose is higher in side A than in side B.
C) The water level is higher in side A than in side B.
D) The water level is unchanged.
E) The water level is higher in side B than in side A.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The presence of cholesterol in the plasma membranes of some animals
A) enables the membrane to stay fluid more easily when cell temperature drops.
B) enables the animal to remove hydrogen atoms from saturated phospholipids.
C) enables the animal to add hydrogen atoms to unsaturated phospholipids.
D) makes the membrane less flexible, allowing it to sustain greater pressure from within the cell.
E) makes the animal more susceptible to circulatory disorders.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The phosphate transport system in bacteria imports phosphate into the cell even when the concentration of phosphate outside the cell is much lower than the cytoplasmic phosphate concentration. Phosphate import depends on a pH gradient across the membrane-more acidic outside the cell than inside the cell. Phosphate transport is an example of
A) passive diffusion.
B) facilitated diffusion.
C) active transport.
D) osmosis.
E) cotransport.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the following questions, match the labeled component of the cell membrane in the figure with its description.
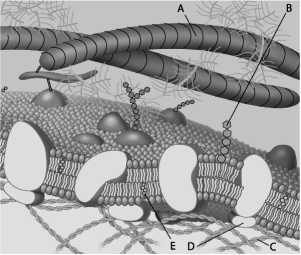 -Which component is cholesterol?
-Which component is cholesterol?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true of integral membrane proteins?
A) They lack tertiary structure.
B) They are loosely bound to the surface of the bilayer.
C) They are usually transmembrane proteins.
D) They are not mobile within the bilayer.
E) They serve only a structural role in membranes.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the following questions, match the labeled component of the cell membrane in the figure with its description.
 -Which component is a microfilament of the cytoskeleton?
-Which component is a microfilament of the cytoskeleton?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is most likely true of a protein that cotransports glucose and sodium ions into the intestinal cells of an animal?
A) The sodium ions are moving down their electrochemical gradient while glucose is moving up.
B) Glucose entering the cell along its concentration gradient provides energy for uptake of sodium ions against the electrochemical gradient.
C) Sodium ions can move down their electrochemical gradient through the cotransporter whether or not glucose is present outside the cell.
D) The cotransporter can also transport potassium ions.
E) A substance that blocks sodium ions from binding to the cotransport protein will also block the transport of glucose.
G) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Some regions of the plasma membrane, called lipid rafts, have a higher concentration of cholesterol molecules. As a result, these lipid rafts
A) are more fluid than the surrounding membrane.
B) are more rigid than the surrounding membrane.
C) are able to flip from inside to outside.
D) detach from the plasma membrane and clog arteries.
E) have higher rates of lateral diffusion of lipids and proteins into and out of the lipid rafts.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the years since the proposal of the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane, which of the following observations has been added to the model?
A) The membrane is only fluid across a very narrow temperature range.
B) Proteins rarely move, even though they possibly can do so.
C) Unsaturated lipids are excluded from the membranes.
D) The concentration of protein molecules is now known to be much higher.
E) The proteins are known to be made of only acidic amino acids.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In receptor-mediated endocytosis, receptor molecules initially project to the outside of the cell. Where do they end up after endocytosis?
A) on the outside of vesicles
B) on the inside surface of the cell membrane
C) on the inside surface of the vesicle
D) on the outer surface of the nucleus
E) on the ER
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a reasonable explanation for why unsaturated fatty acids help keep any membrane more fluid at lower temperatures?
A) The double bonds form kinks in the fatty acid tails, preventing adjacent lipids from packing tightly.
B) Unsaturated fatty acids have a higher cholesterol content and therefore more cholesterol in membranes.
C) Unsaturated fatty acids are more polar than saturated fatty acids.
D) The double bonds block interaction among the hydrophilic head groups of the lipids.
E) The double bonds result in shorter fatty acid tails and thinner membranes.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The sodium-potassium pump in animal cells requires cytoplasmic ATP to pump ions across the plasma membrane. When the proteins of the pump are first synthesized in the rough ER, what side of the ER membrane will the ATP binding site be on?
A) It will be on the cytoplasmic side of the ER.
B) It will be on the side facing the interior of the ER.
C) It could be facing in either direction because proteins are properly reoriented in the Golgi apparatus.
D) It doesn't matter, because the pump is not active in the ER.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
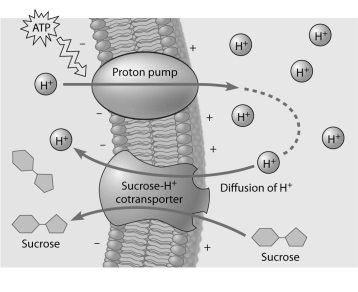 -Based on the figure above, which of these experimental treatments would increase the rate of sucrose transport into the cell?
-Based on the figure above, which of these experimental treatments would increase the rate of sucrose transport into the cell?
A) decreasing extracellular sucrose concentration
B) decreasing extracellular pH
C) decreasing cytoplasmic pH
D) adding an inhibitor that blocks the regeneration of ATP
E) adding a substance that makes the membrane more permeable to hydrogen ions
G) C) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An organism with a cell wall would most likely be unable to take in materials through
A) diffusion.
B) osmosis.
C) active transport.
D) phagocytosis.
E) facilitated diffusion.
G) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements correctly describes the normal tonicity conditions for typical plant and animal cells?
A) The animal cell is in a hypotonic solution, and the plant cell is in an isotonic solution.
B) The animal cell is in an isotonic solution, and the plant cell is in a hypertonic solution.
C) The animal cell is in a hypertonic solution, and the plant cell is in an isotonic solution.
D) The animal cell is in an isotonic solution, and the plant cell is in a hypotonic solution.
E) The animal cell is in a hypertonic solution, and the plant cell is in a hypotonic solution.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Five dialysis bags, constructed from a semipermeable membrane that is impermeable to sucrose, were filled with various concentrations of sucrose and then placed in separate beakers containing an initial concentration of 0.6 M sucrose solution. At 10-minute intervals, the bags were massed (weighed) and the percent change in mass of each bag was graphed.
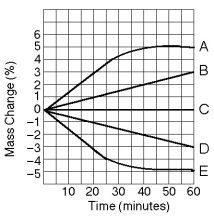 -Which line in the graph represents the bag that contained a solution isotonic to the 0.6 M solution at the beginning of the experiment?
-Which line in the graph represents the bag that contained a solution isotonic to the 0.6 M solution at the beginning of the experiment?
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
G) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cell membranes are asymmetrical. Which of the following is the most likely explanation?
A) The cell membrane forms a border between one cell and another in tightly packed tissues such as epithelium.
B) Cell membranes communicate signals from one organism to another.
C) The two sides of a cell membrane face different environments and carry out different functions.
D) The "innerness" and "outerness" of membrane surfaces are predetermined by genes.
E) Proteins can only be associated with the cell membranes on the cytoplasmic side.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The solutions in the arms of a U-tube are separated at the bottom of the tube by a selectively permeable membrane. The membrane is permeable to sodium chloride but not to glucose. Side A is filled with a solution of 0.4 M glucose and 0.5 M sodium chloride (NaCl) , and side B is filled with a solution containing 0.8 M glucose and 0.4 M sodium chloride. Initially, the volume in both arms is the same. Refer to the figure to answer the following questions.
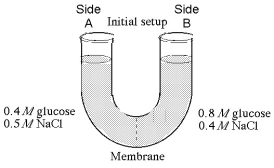 -If you examine side A after three days, you should find
-If you examine side A after three days, you should find
A) a decrease in the concentration of NaCl and glucose and an increase in the water level.
B) a decrease in the concentration of NaCl, an increase in water level, and no change in the concentration of glucose.
C) no net change in the system.
D) a decrease in the concentration of NaCl and a decrease in the water level.
E) no change in the concentration of NaCl and glucose and an increase in the water level.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 80
Related Exams